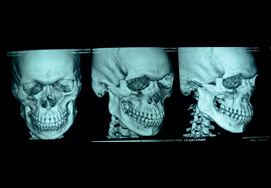
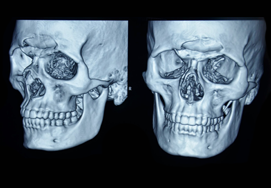
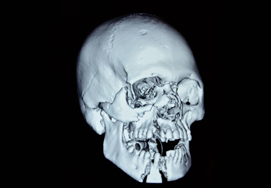
Mandible Fracture
Liposuction, also known as lipoplasty, slims and reshapes specific areas of the body by removing excess fat deposits, improving your body contours and proportion, and ultimately, enhancing your self-image.

- What is a mandible fracture?
- What are the symptoms of lower jaw fracture?
- What are the types of surgeries?
- How should I prepare for the surgery?
- What will happen during the surgery?
- What is the aftercare of the surgery?
- What are the postsurgical considerations?
What is a mandible fracture?
Mandibular fractures, also known as fractures of the jaw, are breaks through the mandibular bone.
Mandibular fractures are especially common in young men. The fractures may be due to road accidents, assaults, falls, industrial injuries, or sports injuries.
Usually, the mandibular fractures occur at the parasymphyseal area, symphyseal region, horizontal ramus, condylar neck, and mandibular angle.
What are the symptoms of lower jaw fracture?
The two most common symptoms described are pain and the feeling that teeth no longer correctly meet (traumatic malocclusion).
The teeth are very sensitive to pressure (proprioception), so even a small change in the location of the teeth will generate this sensation. Patients will also been very sensitive to touching the area of the jaw that is broken, or in the case of condylar fracture the area just in front of the tragus of the ear.
Loose teeth (teeth on either side of the fracture will feel loose because the fracture is mobile), numbness (because the inferior alveolar nerve runs along the jaw and can be compressed by a fracture) and trismus (difficulty opening the mouth) are other symptoms.
What are the types of surgeries?
Simple fractures are usually treated with closed reduction and indirect skeletal fixation, more commonly referred to as maxillo-mandibular fixation (MMF). The indirect skeletal fixation is accomplished by placing an arch bar, secured to the teeth on the maxillary and mandibular dentition, then securing the top and bottom arch bars with wire loops.
Closed reduction and Intermaxillary fixation– If the fracture is minimally displaced and you agree for a period of 6 weeks for your mouth to be closed then the fracture can be managed with minimal intervention of intermaxillary fixation. The jaw is immobilized so that it can heal in proper postion. This is referred to mandibulo-maxillary fixation (MMF). So, the surgeon keeps the jaw shut (using arch bars) by wiring the upper and lower jaw for several weeks for dentate patients. Another method of treating the fractured jaw includes screwing metal plates into the jaw bone on each side of the fracture.
In case of partially edentulous patients, the partial denture is used for intermaxillary fixation and in case of edentulous patients, the denture is secured first using circum-mandibular wires or palatal screws.
Open reduction: osteosynthesis with plate fixation is done in open reduction.
Open reduction with direct skeletal fixation allows the bones to be directly manipulated through an incision so that the fractured ends meet, then they can be secured together either rigidly (with screws or plates and screws) or non-rigidly (with trans osseous wires). There are a multitude of various plate and screw combinations including compression plates, non-compression plates, lag-screws, mini-plates and biodegradable plates.
External fixation, which can be used with either open or closed reduction uses a pin system, where long screws are passed through the skin and into either side of a fracture segment (typically 2 pins per side) then secured in place using an external fixator. This is a more common approach when the bone is heavily comminuted (shattered into small pieces, for instance in a bullet wound) and when the bone is infected (osteomyelitis).
Regardless of the method of fixation, the bone need to remain relatively stable for a period of 3–6 weeks. On average, the bone gains 80% of its strength by 3 weeks and 90% of it by 4 weeks. There is great variation depending on the severity of injury and health of the wound and patient.
How should I prepare for the surgery?
Before the surgery, your surgeon may advise you need to follow certain instructions:
- Blood workup, radiographs , viral screening , appropriate CT scans need to be done
- Pre anaesthetic check up has to be done
- Avoid substances that cause allergy
- Quit smoking and drinking
- Sleep well and also try to do some physical exercises
- Stop eating or drinking for six hours before your surgery
- Notify your surgeon if you have any illness like cold, cold sore, stomach or bowel upset
What will happen during the surgery?
The surgery may be performed through different approaches such as intraoral, submandibular, retromandibular, and preauricular.
In case of intraoral approach, surgery is easy to perform; there will be no scar formation and less risk to the facial nerve.
The surgery of closed reduction with arch bars is described below:
For simple fractures – occlusion is relatively simple to achieve. So here closed indirect reduction is sufficient.
Arch bars or braces are placed on the teeth, which are manipulated to allow them to come in occlusion, intermaxillary fixation is done after occlusion is achieved.
The surgery of plate fixation is described below:
Surgery is done under general anaesthesia. Lower buccal sulcus degloving approach splitting the mentalis muscle obliquely is used to expose the mandibular fracture of the symphysis , body and angle which is reduced and fixed with plates and screws.
Retromandibular approach is used for subcondylar fractures. Fixation is done after reduction with plates and screws.
What is the aftercare of the surgery?
Oral hygiene has to maintained which is very essential for healing of fracture without infection.
Mouth wash and rinse to be done after every meal and regular intervals
Brushing of teeth to be done at regular intervals.
The typical healing time for a mandibular surgery is 4 to 6 weeks. You need to follow-up with your plastic surgeon regularly for a healthy and speedy recovery.
After the surgery, if your jaw may be kept wired if deemed necessary you may not be able to eat food. So, you have to take the fluid diet using a straw. It is recommended to have soft foods until the jaw heals.
If there is a sensation of vomiting, cut the wires immediately as the vomit should not be swallowed. It is beneficial for you to carry wire cutters all the time.
What are the postsurgical considerations?
The complications of the surgery may include:
- Mal occlusion
- Malunion
- Increased caries incidence
- Dental root injury