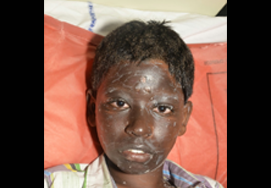
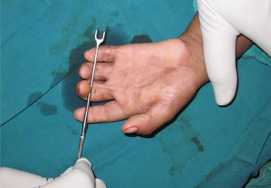
Burn Wounds Management
Recommended for the individuals with unhealed burn wounds; deep burn wounds; scar contractures causing limited motion of the neck, shoulder, hands, or legs; and scarring causing deformity on the eyelids, lips, nose, or scalp

- What is Burn Wounds Management?
- What is reconstructive burn surgery?
- What are the types of the surgeries?
- Which individuals are suitable for the surgery?
- How should I prepare for the surgery?
- How should I prepar What happens during the surgery?
- What is the aftercare of the surgery?
- What are the postsurgical considerations?
What is Burn Wounds Management?
A burn wound is an injury caused by thermal, chemical, electrical or radiation energy. A scald is a burn caused by contact with a hot liquid or steam but the term ‘burn’ is often used to include scalds.
Burn wound care is essential to prevent infection and promote healing process.
Most burns heal without any problems but complete healing in terms of cosmetic outcome is often dependent on appropriate care, especially within the first few days after the burn. Most simple burns can be managed in primary care but complex burns and all major burns warrant a specialist and skilled multidisciplinary approach for a successful clinical outcome.
BURN WOUNDS
Burn wounds can result from exposure to flames, hot objects, hot liquids, chemicals or electricity.
Burn wounds are Burns vary in depth depending on the duration of contact with heat and temperature of contact. Degree of Burn wound depth determines how they need to be managed.
First-degree burns are also known as superficial burns because the only affect the outermost layer of skin, the epidermis. The skin will become red, dry and painful but eventually the epidermis layer will come off. First-degree burns typically don’t require medical care and tend to heal spontaneously
Second-degree burns usually extend to the dermis layer, and can be superficial partial thickness or deep partial thickness in depth.
Superficial partial thickness burns affects the epidermis and the dermis, though the damage second layer is superficial. These may be moist and red and could form blisters. These burns require great care to prevent them from becoming infected and scarring
Deep partial thickness burns extend fully through the two layers of skin but may be less painful and red than the superficial. However, they take longer to heal and can have more scarring. Second degree burns most likely require medical attention in form of skin grafts
Third degree burns extend through the entire dermis and cause the skin to become stiff and turn white or brown in colour. They can take months to heal and require burn wound care. These require reconstructive surgery in form of Flaps or skin grafts
Fourth degree burns extend through the entire skin and as well as the underlying fat, muscle and bone. The skin will turn black and look charred. Fourth degree burns are the most serious and require immediate medical attention and treatment.
Second-degree burns require skin grafts
Third and fourth, require reconstructive surgery in form of skin grafts and Flaps
What is reconstructive burn surgery?
Reconstructive burns surgery involves a lot of thinking and a lot of attention to detail and requires to be individualized for the patient, as no two burn patients are alike or their problems alike.
The aim of the surgery is to improve the function and aesthetic appearance of burn wounds and reduce the formation of burn contractures and scars. The timely management of burn wounds reduces the formation of hypertrophic scars and contractures helps to achieve healing in a timely fashion, preserve function ability and to minimize cosmetic deformity.
If you are suffering from severe burn wounds that resulted in limited mobility, loss of sensation, and unappealing look, then plastic surgery would be the best option.
What are the types of the surgeries?
There are different types of cosmetic surgical techniques used to treat burn wounds. Your surgeon would suggest any of these techniques based on the severity of the wound.
Collagen sheet application
This is a type of dermal sheet, which provides a mechanical barrier, decrease fluid an electrolyte losses, decreases pain, allows faster healing of burns wounds. Burn wound tend to heal with less scarring and have a more pleasing result as wounds tend to heal with less infection.
These are generally applied to superficial second-degree burns, which can heal by themselves provided they do not get infected.
Skin grafts: The skin grafting is the most common procedure used to treat burn injuries. The surgery involves removing the skin from one area of the body and is transplanted to the burnt region. There are two types of skin grafts:
- Split-thickness grafts- in this technique, a few layers of outer skin are transplanted. The donor area tends to heal within 2 weeks
- Full-thickness grafts- this technique involves removal of the whole dermal layers of the skin. Donor area is either closed primarily by direct approximation or skin grafted. The limitation is availability of full thickness graft is limited
Microsurgical flap procedure: Microsurgery in burns is used to improve outcomes in difficult cases where vital structures are at risk or vital function is at risk. Microsugery is used to bring vascularised tissues to cover areas which are not likely to heal by skin grafts. They are superior to local flaps in burns as in most cases local flaps will not be available or inadequate for the proposed purpose.
Tissue expansion: This technique is used to address and resurface burn scars once formed to improve appearance and function. The procedure enables your body to grow extra skin for use in resurfacing scars and reconstruct certain lost parts. This involves inserting an instrument called “balloon expander” under the skin near the area that requires a repair. Over time, the balloon will be gradually filled with saline solution, slowly causing the skin to stretch and grow. This is similar to a woman’s skin stretching during pregnancy. Once the skin is grown, it is used to correct or reconstruct the damaged body part.
Which individuals are suitable for the surgery?
Reconstructive burn surgery is recommended for the individuals with:
- Unhealed burn wounds
- Deep burn wounds
- Hypertrophic and mature Scar contractures causing limited motion of the neck, shoulder, hands, or legs
- Scars Causing deformity on the eyelids, lips, nose, or scalp
- Hypertrophic scars (i.e. Scars which are abnormal – raised red and itchy scars)
Skin grafts are usually employed in the patients with severe burn injuries that result in skin damage.
Flap surgery is recommended in patients who have suffered tissue loss over any area of the body where skin grafts cannot be used or are not the best reconstructive option.
How should I prepare for the surgery?
Your doctor will give you specific instructions before the surgery which include the following:
- Anaesthesia works up has to be completed.
- Get your blood workup and anaesthetic workup done prior to surgery
- Avoid taking medications like aspirin to prevent the risk of internal bleeding
- Avoiding certain herbal supplements that may interfere with your recovery
- Avoid eating or drinking few hours before the surgery as empty stomach reduces the risk of nausea caused by anaesthesia.
How should I prepar
What happens during the surgery?
Skin graft is the common cosmetic surgical technique performed to treat the patients with burn wounds. Your surgeon will inject general anesthesia that makes you fall asleep and stays asleep throughout the surgery.
The surgeon then removes the skin from the donor site using a special skin-cutting instrument called as “dermatone”. For split-level thickness graft, the surgeon will remove skin from the areas such as your hip or the inside of your thigh as these areas are hidden under the clothing. For a full-thickness graft, the surgeon removes the skin from abdominal wall or the chest wall.
After removing the skin from the donor site, the surgeon carefully places it over the transplant area and secures it with a surgical dressing, staples, or stitches. Then the donor area is covered with a surgical dressing.
Recovery of split-thickness skin graft and full thickness grafts often takes less than three to four weeks
e for the surgery?
Your doctor will give you specific instructions before the surgery which include the following:
- Anaesthesia works up has to be completed.
- Get your blood workup and anaesthetic workup done prior to surgery
- Avoid taking medications like aspirin to prevent the risk of internal bleeding
- Avoiding certain herbal supplements that may interfere with your recovery
- Avoid eating or drinking few hours before the surgery as empty stomach reduces the risk of nausea caused by anaesthesia.
What is the aftercare of the surgery?
After undergoing any surgery which involves removal and transplantation of the skin, it is very important to follow the general instructions and guidelines for proper wound care.
- Your surgeon will prescribe certain medications which include pain killers to help minimize the pain.
- You should avoid doing activities that could stretch or injure the surgical site for at least three to four weeks after the surgery.
- You can resume your daily activities after complete healing of the surgical site.
- You may be required to wear pressure garments to help the skin graft settle down
- You will have to apply coconut oil or Vaseline to help moisturize your new skin graft
- You will have to do physiotherapy to improve your range of motion.
- You may require to use some splint as advised by the doctor.
What are the postsurgical considerations?
Be patient with your healing after the surgery that repairs burns or wounds completely. As you continue to heal you will notice changes in the colour, appearance of the skin and tingling sensation at the surgical site. Do not worry as this condition is normal and fades off in few weeks.
Skin grafts will mature with time, so you require to be patient and their texture and colour will improve with time. Massaging a skin graft will help in graft maturation.