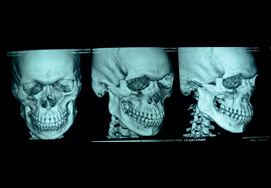
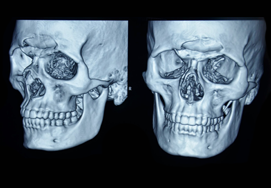
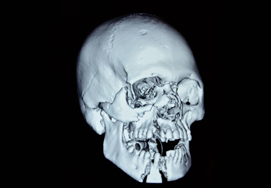
Fracture Frontal Bones
The Frontal Bone fracture is rather rare and serious if occurs, due to the danger it poses to the brain. It may lead to meningitis, cerebral abscess, and encephalitis if left untreated.

- What is a frontal bone fracture?
- What is an anterior table fracture?
- What is a posterior table fracture?
- What are the types of surgeries?
- How to prepare for the surgery?
- What will happen during the surgery?
- What is the aftercare of the surgery?
- What are the post surgical considerations?
What is a frontal bone fracture?
Forehead region is supported by the frontal bone below. Frontal bone is subcutaneous in position and is easily injured in any accident. As it forms a prominent portion of the face. Fractures and soft tissue injuries on the forehead result in a visible scarring and deformity.
Fracture of the frontal bone result from blunt or penetrating injury. Blunt injuries are far more common, resulting from vehicular accidents, altercations, sporting-related trauma, occupational injuries, and falls. Frontal bone is in close proximity to the brain, so fractures are usually associated with underlying brain injury. However, if these fracture in this area is not treated in a proper way, along with plastic surgeon. Gross deformities of the face result. Which are visible and prevent the social integration of the patient in the society due to lack of self-confidence.
A fracture involving frontal bone has a potential for underlying head injury and should be managed effectively because it is located close to the brain. Frontal fractures can occur in isolation or in association with multiple facial fractures, or in polytrauma.
Frontal bone has two tables- Anterior table and posterior table. Anterior table is near the skin and the posterior table is near the brain, and in between is the frontal sinus which drains through naso lacrimal duct into the nose.
The following are the crucial areas that are generally addressed in this type of fracture:
- Anterior table fracture- this occurs with or without displacement and outflow tract injury
- Posterior table fracture- this commonly occurs in combination with anterior table fracture
- Displacement- this is considered to be present if it is about the width of one table of the frontal bone.
When there is posterior table fracture with CSF leak, then the patient is considered as head injury patient.
The common problems with of fracture frontal bone are:
- Cosmetic defect
- Severe headache
- Leakage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – this is mostly seen in patients with posterior table fractures.
- Injury to naso frontal duct
- Injury to the frontal lobe of the brain
What is an anterior table fracture?
Undisplaced fracture is generally managed without surgery.
Displaced fractures greater than 1 to 2 mm have an increased risk of aesthetic deformity and require surgical intervention to prevent deformity .
Bone grafting and frontal sinus obliteration can manage anterior table fractures of the frontal bone with severe communition and marked mucosal injury.
What is a posterior table fracture?
These fractures which are not displaced and without CSF (Cerebro spinal fluid) leak can be managed with frontal sinusotomy, and if there is Cerebro Spinal Fluid leak, Frontal sinus obliteration is indicated.
For displaced fractures without CSF leak, osteoplastic flap with and sinus obliteration is recommended. If there is CSF leak, patients should undergo open exploration with an osteoplastic flap.
- Assessments required: A computed CT scan is the gold standard for the assessment of the forehead fractures. Patients are scanned in the axial plane in supine position,
- creating data set allowing generation of reformatted and reconstructed diagnostic images.
- To evaluate the posterior wall defect, sagittal reconstructions can also be made.
- A complete ophthalmic examination is done to check the eye injury.
- The consciousness of the patient should be checked carefully to determine the intracranial complications.
- Other injuries should be looked for because force necessary to cause the fracture is enormous.
What are the types of surgeries?
The goal of the treatment is to correctly align the frontal bone fracture fragments to prevent secondary deformity and bridge any bony gaps.
Surgical approach through traumatic wounds
In exceptional cases, an existing traumatic wound is used to address an isolated fracture of the anterior frontal sinus wall. It is considered in limited injuries without the involvement of the frontal sinus or in the absence of other associated regional craniofacial injuries.
Surgical approach through Bicoronal incision
The purpose of this surgical approach is to avoid facial scars, provides wide exposure of the fracture, allowing excellent reduction and fixation. The extent and design of the incision depend on the targeted anatomic area and intended surgical procedure. The coronal incision allows harvesting of the calvarial bone graft when required.
How to prepare for the surgery?
Most of the forehead bones fracture surgeries are performed on an emergency basis as these types of fractures occur during accidents. The surgeon will give some basic instructions that you need to follow strictly before the surgery.
- Blood tests, urine tests, chest Radiographs, ECG and CT scans require to be done
- Anesthetic fitness requires to be done so that your anaesthesia is safe and well monitored.
- Informed consent requires to be signed.
What will happen during the surgery?
The bicoronal incision is usually performed if the forehead bone fracture is intact without skin incision. The patient will be operated under general anesthesia. The patients head requires to be shaved or at least around the area of incision so that surgical area is clean. After disinfecting and draping the surgical area, the planned zig zag line of incision is marked with a surgical pen. Then a 2% lignocaine with 1:200 000 adrenaline was infiltrated in the area to achieve vasoconstriction and to get fluid dissection.
Along with this sometimes a running stitch is given along the posterior border of intended incision. This is done to avoid bleeding as the vascularization of the scalp is very rich and can bleed profusely when cut. Then the surgeon makes incision over the planned area to the proper depth and pulls the scalp forward with a pair of cat paw retractors, and dissects the flap by reverse cutting with a large blade until it turns inside out.
Then he makes a small hole over the fractured segment of bone. The fractured fragment will be are reduced and fixed with micro mini plates or mesh depending upon the comminution of the fracture.
What is the aftercare of the surgery?
Soon after the surgery, you will be moved to the intensive care unit (ICU). Your condition will be monitored regularly until you get discharged from the hospital.
- After discharge, you should take plenty of rest and avoid stressful situations.
- Avoid drinking alcohol and other illegal drugs
- You can take paracetamol if you have a headache, but try to avoid nonsteroidal anti inflammatory drugs like aspirin unless prescribed by your physician.
- Avoid playing contact sports like football for at least 2 months , and talk to your doctor before starting to play these games again.
- Do not return to daily activities like going to the office or work until you recover completely and feel enough to do so.
- Avoid driving car or motorbike or operate machinery until you have recovered fully.
- Do not forget to keep track on follow-up appointments of your surgeon. Follow the surgeon’s instructions religiously and follow up at regular intervals.
What are the post surgical considerations?
Like any surgery, this procedure also has risks such as cause pain, swelling, bruising, and infection.
Bleeding can also be seen in some cases.
There will be post operative facial swelling which usually subsides in a few days.
You may have drain placed beneath your scalp which is removed in 24 to 48 hours after surgery.
Sutures are usually removed within a week .